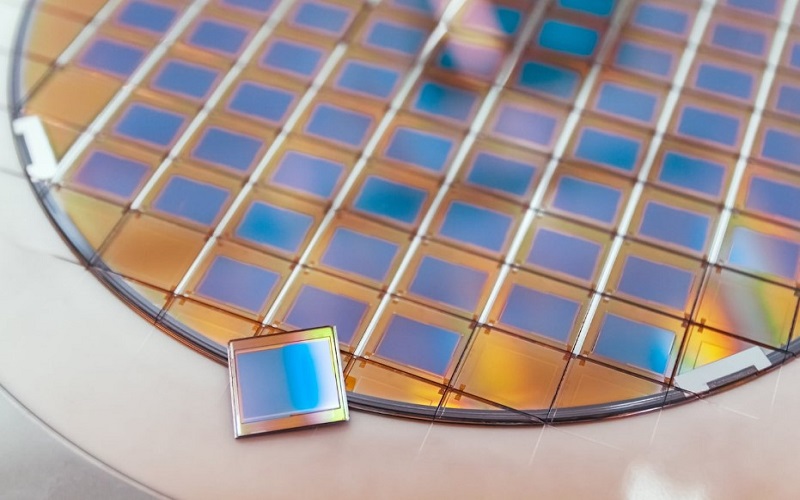
Wafer dicing, also known as die singulation or wafer sawing, is a crucial process in semiconductor manufacturing. It involves cutting a semiconductor wafer into individual chips or dice, each containing one or more integrated circuits (ICs) or electronic components. The primary purpose of wafer dicing is to separate the multiple devices that have been fabricated on a single semiconductor wafer into discrete, functional units that can be further processed and packaged. Here’s a more detailed explanation of wafer dicing:
Key Aspects of Wafer Dicing:
-
Starting Material: The process begins with a semiconductor wafer, typically made of silicon. These wafers are circular, flat substrates on which ICs and other electronic components are manufactured.
-
Multiple Devices: Semiconductor wafers are usually fabricated with numerous identical or diverse ICs arranged in an array across the wafer’s surface. These devices share a common semiconductor material.
-
Methods: There are two main methods of wafer dicing:
- Blade Dicing: In this method, a thin, high-speed rotating blade, often embedded with abrasive particles, is used to mechanically cut the wafer along predefined lines or scribe lines.
- Laser Dicing: Laser dicing employs a high-energy laser beam to ablate and separate the material along the cutting path. It is a non-contact method and is suitable for delicate materials and precise cuts.
-
Purpose: The primary purpose of wafer dicing is to transform a single semiconductor wafer, which contains multiple ICs, into individual chips or dice. Each chip can then be packaged and used as an individual electronic component.
-
Quality Control: Precision and quality control are crucial in wafer dicing to ensure that the individual chips meet the required specifications. Inspection and measurement techniques are employed to verify dimensions, alignment, and quality.
-
Equipment: Specialized dicing equipment, such as dicing saws for blade dicing and laser dicing machines for laser dicing, is used for this process. These machines are equipped with precise control mechanisms to ensure accurate cuts.
-
Scribing: Before dicing, scribe lines are created on the wafer’s surface. These lines serve as guides for the dicing process, ensuring that the cuts are made precisely according to the design specifications.
-
Post-Dicing Cleaning: After dicing, the individual chips are typically cleaned to remove any debris, particles, or residues left from the dicing process. Clean chips are essential for reliable packaging and assembly.
-
Packaging: Once the chips are diced and cleaned, they are placed into semiconductor packages, which provide electrical connections, protection, and mechanical support for the chips. The type of package used depends on the specific application.
-
Testing: Packaged chips undergo electrical testing to ensure they function correctly. Testing may include functionality tests, parametric tests, and other quality control measures.
In summary, wafer dicing is a critical step in semiconductor manufacturing that involves cutting a semiconductor wafer into individual chips, which can then be packaged and used in electronic devices. It requires precision, quality control, and various methods to achieve the desired results.